Polyethylene (PE) is a commonly utilized packaging polymer, especially in bottling. PE Grade for Bottles takes the highest priority due to polyethylene grades with varying properties for specific applications. For bottling, performance optimization, cost savings, safety, and appearance are made possible by knowing the polyethylene grade. High-Density Polyethylenes are renowned because of their great capsule-making properties, making them a preferred option. Hence, they are of great importance in capsule making. They are also essential in the portable packaging sector, especially in the fields of milk, detergent, and juices. They serve easily because of their efficiency and strength. Moreover, MDPE, LDPE, and LLDPE are capable materials and are also aesthetically pleasing, making them perfect for economic use. They also serve perfectly in versatility. The summary here will mainly focus on why High-Density Polyethylenes are essential in capsule making.
An understanding of these differences enables manufacturers to make the ideal HDPE blow molding Grade choice in a compromise between performance and costs, as well as safety considerations.

Overview of PE & Its Grades
Despite having different grades each with its own distinct molecular structure and weight, Polythene remains a highly versatile polymer. These different grades and their common forms include, but are not limited to, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and its constituent grades, Low and Medium polymers (LDPE, MDPE, LLDPE), and several others such as Ultra High molecular weight Polyethylene and Bio Polyethylene.
HDPE, with its weight categorized between 0.941 to 0.965 g/cm cubed, being a branched, highly crystalline polymer, tends to be tough and rigid. Its polymer makes line pipe with blow mode molds, which serves as a chemical and force-resistant industrial-grade pipe. MDPE, with a weight ranging between 0.926 and 0.940 g/cm cubed, being moderately branched, is flexible enough yet stiff and tough for grade A rugged packaging. LDPE, on the other hand, with a weight range of 0.910 to 0.940 g/cm cubed, is highly flexible in the form of films and squeeze bottles as it is long-branched and polymerized. LLDPE is a low-density type but is distinguished by short, uniform chains. It possesses a blend of flexibility with higher tensile strength and is mainly used for film packaging and flexible packaging.
|
PE Grade
|
Density (g/cm³)
|
Branching Type
|
Crystallinity
|
Typical Use in Packaging
|
Mechanical Properties
|
|
HDPE
|
0.941-0.965
|
Minimal (short-chain)
|
High
|
Rigid Bottles, Blow Molding
|
High Stiffness, Impact Resistance
|
|
MDPE
|
0.926-0.940
|
Moderate
|
Medium
|
Flexible Bottles, Pipes
|
Moderate Stiffness, Good Toughness
|
|
LDPE
|
0.910-0.940
|
Long-chain
|
Low
|
Films, Flexible Containers
|
Soft, Flexible, Good Clarity
|
|
LLDPE
|
0.915-0.925
|
Short-chain
|
Low
|
Films, Flexible Packaging
|
Improved Strength & Flexibility
|
Detailed PE Grades Used in Bottles
In the packaging market, the correct selection of PE Grade for Bottles is imperative to realize optimal product performance, safety, and cost savings.
Of the polyethylenes, HDPE blow molding Grades are market leaders for the rigid bottle market due to their superior mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and food contact compliance. Such vendors as Shobeir Shimi become indispensable as they supply a range of high-density polyethylene grades for blow molding specifically formulated for making bottles.
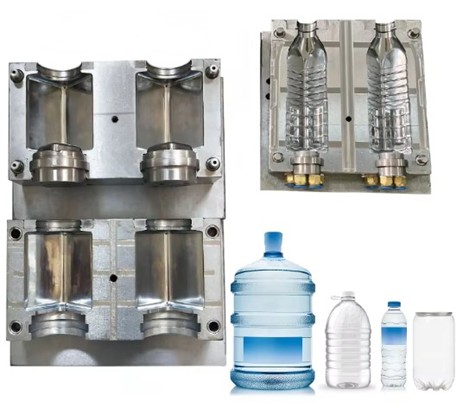

HDPE Blow Molding Grade for Bottles
The most common type of polyethylene used in the rigid bottle is HDPE, more specifically, in its HDPE blow molding Grade. This grade is formulated to have high crystallinity, which provides it with good stiffness and impact resistance, and is hence the best for application in containers requiring stiffness and hardness. For instance, HDPE blow moulding grades such as HD-0035, HBM5520, HBM5020, HBM-5510, and BL3 are designed to meet the diverse demands of milk bottle manufacturers. They are generally used in making milk bottles, detergent tanks, chemical drums, and shampoo bottles because HDPE is moisture and a wide variety of chemical-resistant yet food-safe compliant. The phrase "bottle grade HDPE" also generally speaks not only of material performance properties but of recycling streams, so material recovery and reuse in circular economies are more at hand.
LDPE in Bottle Manufacturing
Though LDPE is less common in rigid bottles due to its being flexible as well as not nearly as durable, it is behind applications requiring softness and squeezability. The long-chain branching provides the ability to be incredibly flexible, and this makes LDPE particularly suited to squeeze bottles, dropper bottles, and stretchy caps. Its softness and clarity of LDPE provide cosmetics and pharmaceuticals packaging with tactile and visual appeal, although it is not typically suited for bottles that require structural rigidity.

MDPE and LLDPE: Intermediate and Flexible Uses
MDPE or Medium-Density Polyethylene falls in between HDPE and LDPE. With a density ranging from 0.926 to 0.940 g/cm³, MDPE is tougher than HDPE but less rigid. Less commonly used in the manufacture of bottles, MDPE is used for the manufacture of closures, films, and parts of flexible containers due to its toughness and resistance. Use in the manufacture of rigid bottles is small but not insignificant. LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) has the same flexibility as LDPE but higher tensile strength due to short, regular branching. LLDPE is used sparingly in totally rigid bottles but appears often in flexible packaging and parts that require elasticity and tear resistance. It appears in caps or flexible segments molded into bottles.
Practical Implications and Industry Use
End-use application needs determine polyethylene bottle grade selection. HDPE blow molding Grade remains the benchmark for rigid containers that require strength, chemical resistance, and food safety. Shobeir Shimi is among those companies that offer grades tailored to meet customers' individual needs, balancing ease of processing with mechanical properties to allow producers to produce high-quality bottles at an affordable price. Additionally, the survey allows for the term "bottle grade HDPE" to explicitly enable recycling since post-consumer HDPE bottles are collected, sorted, and recycled under this designation, promoting sustainability.
Key Properties & How They Relate to Bottle Requirements
Proper selection of PE Grade for Bottles depends on the identification of the important properties to meet bottle specifications. Stiffness and rigidity are necessary to support structure, in which HDPE blow molding is highly suitable since it is extremely dense and crystalline.
Resistance to impact, necessary for drops and handling, is just as strong in High density polyethylene grade for blow molding due to its toughness. Chemical resistance is especially important in bottles used with cleaning chemicals or acids; HDPE's non-polar character gives excellent protection. Barrier properties to water and oxygen vary; HDPE gives moderate barriers, while LDPE is more permeable. Appearance properties like gloss or opacity are grade-related; HDPE is opaque with a superior surface finish, while LDPE gives more clarity and flexibility. Food safety requires non-toxicity and compliance with regulations, and several HDPE grades for blow molding ensure these requirements. Melt flow index is one of the processing conditions that influence molding temperature, flow, and evenness of walls; thus, polyethylene grade selection is critical to efficient bottle manufacturing.
Food Safety / Standards / Regulatory Considerations
PE Bottle Grade is regarded as food grade by being safe with certifications such as FDA (US), EU food contact law, and BIS standards. They govern permissible additives, contaminants and require migration testing to be safe. Coloring agents and pigments must be nontoxic and conform to avoid effect on taste or flavor. HDPE blow molding Grades are generally followed by the resin identification code #2 for recycling and safety approval. Regulatory standards also specify maximum temperature exposure and chemical compatibility, thereby keeping bottles safe in consumers' hands.
Choosing a high-density polyethylene grade certified for blow molding ensures compliance with these strict safety standards.
Manufacturing & Processing Impacts on Grade Choice
PE Bottle Grade choice is heavily influenced by process type. In HDPE blow molding, the design of wall thickness, mold, and cooling rates all depend on the melt flow index of the polyethylene grade. The high MFI grade is flowing freely, which can provide thin walls and faster cycle time, but may reduce strength. The lower MFI grades increase toughness but use more power and longer cycles. Add-on processes like printing or coating may necessitate grades of specific thermal properties or with certain surface finish appearances.
Cost and yield to production are affected as HDPE blow molding Grade material tends to be more costly than LDPE but offers a better performance, which affects overall manufacturing economics.
Trade-offs & Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor in choosing PE Grade for Bottles. HDPE raw material is more expensive than LDPE or LLDPE but has higher durability and recyclability, and potentially lower lifecycle cost. Flexible, lower-cost LDPE helps squeeze containers, while rigid containers are worth HDPE's increased cost with increased strength. Aesthetic applications, for instance, clarity, can require special grades, incurring additional cost. Manufacturing efficiency is different; HDPE tends to take longer cycle times but delivers robust, resilient bottles with less scrap, optimizing cost for performance.
Environmental & Recyclability Aspects
Recyclability is an important advantage of HDPE blow molding Grades, as bottle-grade HDPE finds widespread applicability in recycling streams. Its green profile benefits from lower manufacturing energy and emissions compared to other plastics. However, recycling resin will compromise mechanical performance or generate color/contaminant issues.
Improvements like bio-based PE and PCR (post-consumer recycled) polyethylene grades contribute to greater sustainability without a loss of performance.
Conclusion of PE Grade for Bottles
Choosing the correct PE Grade for Bottles use involves a compromise between toughness, impact resistance, chemical safety, and cost. HDPE blow-molding grade remains the optimum option for hard, hard-wearing bottles, while LDPE works for flexible or squeezable packages. MDPE and LLDPE have niche applications when there is a requirement for moderate flexibility or toughness. Food safety approvals and regulatory sanctions are required in all cases. In the coming times, grades that are balanced in terms of performance and recyclability, like bio-based and PCR grades, will lead the market.
 icons at the top
right corner of the subsection.
icons at the top
right corner of the subsection.